Capacity planning in production

The efficiency of the production process is very dependent on sound capacity planning. The modern capacity planning in the ABRA Gen information system can help you maximize the use of your production resources.
What is Capacity Planning?
Capacity planning is a system of production task planning within the capacity grid so as to render the tasks viable. In the ABRA Gen system, production resources are designated as capacity units. These correspond to real machines, production lines, employee teams, etc. They are organized by site and can be assigned shifts. The system provides an overview of their availability for production at all times.
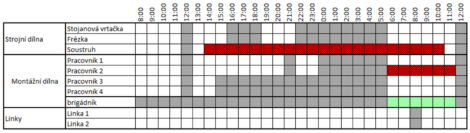
What is a Capacity Grid?
In planning, we use the capacity grid – you can visualize it as a page from a daily planner or graph paper, mapping the availability of individual production resources in time. You can define regular rules as well as various exceptions, such as temporary decommissioning of a machine or an increase of capacity using temp workers.
Recording Production Tasks
First, you need to define the technological procedures within the production order, which determine what should be done, the site and duration of the task. The system will use these to fill in the capacity grid so as to make production viable. The system also takes other predefined rules and facts into account. Each task requires certain conditions to be fulfilled, e.g. it must respect the chronological order of operations. The system can recognize sequential operations and plan everything accordingly so that they remain in the correct order.
Example: When making a stew, you cannot change the chronological order of the procedure to first fry the onion and then dice it.
Capacity Unit Competencies
Capacity units can be assigned competencies, i.e. things they can do, or to what extent they can do them. When planning, the system will choose the capacity units to use according to their specific competencies.
Example: A workshop has three drilling machines. One can drill a diameter of 0-20mm, the second can drill up to 30mm, and the third up to 50mm. For the drilling operation, you can define a competency requirement. For example, I need to drill a hole 25mm in diameter.
Planning according to Material Availability
Every operation is dependent on material supply. When planning operations, ABRA Gen can compile a list of storage cards necessary for the operation. Under the plan, it will create a timeline of availability for all materials using the SCM development. It usually begins with inventory, then takes into account orders and anticipated deliveries. The material timeline shows when the required amount will be available. Then the system uses this information to plan production.
Operation Properties for an Optimal Plan
You can specify multiple properties for the operations. These determine how to plan the individual operations. Properties include the coordination rate, which enables you to divide the task into multiple capacity units; the authorization to interrupt the activity while a different activity is ongoing; and the length of the shortest uninterrupted segment, i.e. the shortest continuous available capacity.
Planning Methods
There are two basic planning methods:
- Forward planning: The system will search for the nearest date with free capacity and the conditions for the first operation, followed by further operations until the production task is finished.
- Backward planning The end date for the production task is determined first; the system then searches for free capacity and sets the start date so that the deadline can be met.
Planning for Limited and Unlimited Capacity
Planning for limited capacity determines that one capacity unit (a square in the capacity grid) can be used for a single production task only. On the other hand, planning for unlimited capacity allows for capacity reuse. This can come in handy if you need to include a very high priority document; you can resolve the capacity overload by increasing capacity or moving the operations by hand.
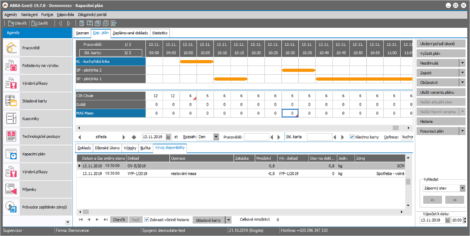
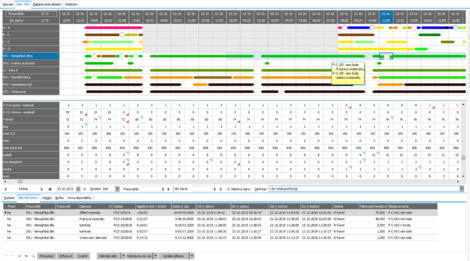
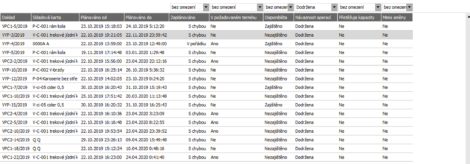
Plan Outputs
- Graphic representation of the plan – a filled-in capacity grid.
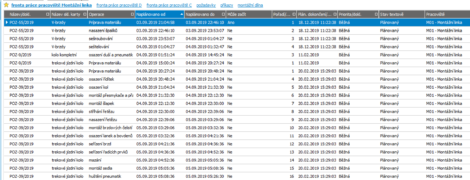
- A list of documents included in the plan with summary information whether all tasks within the order are planned correctly.
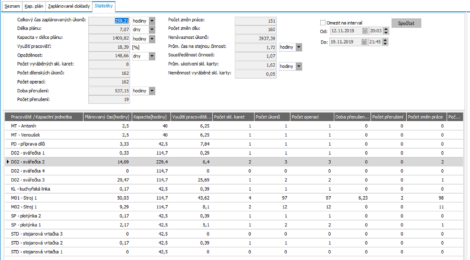
- Summary statistics reflecting the efficiency of the plan.
- Work queue in the Workshop Plan agenda. This instructs the workshop what needs to be done next.
- Information for other agendas in the ABRA Gen system. The system always has up-to-date information from production and can order the necessary materials, create a delivery note, etc.